5 Key Benefits of BIM Drafting Services for Construction
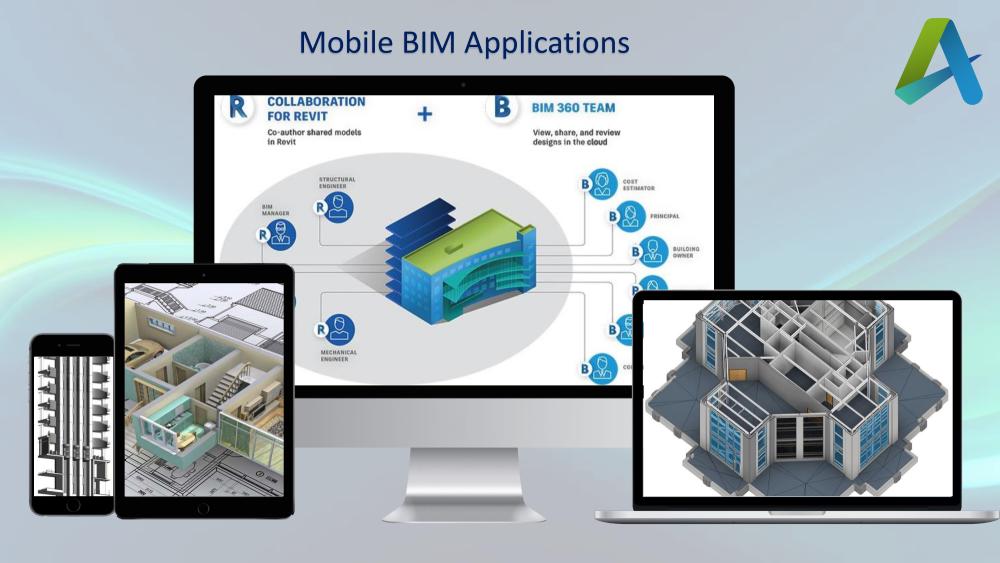
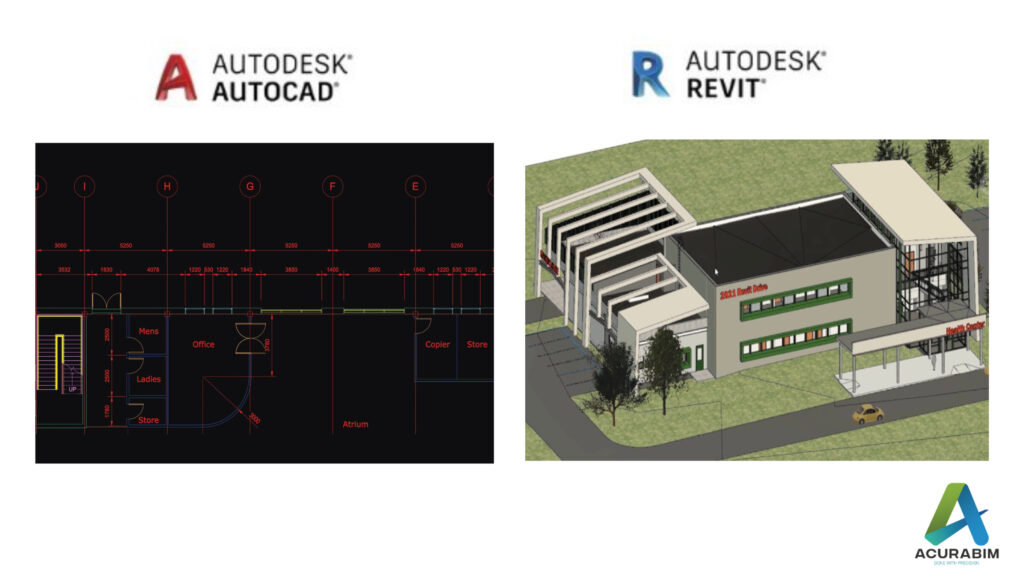
Why, Where, and What: A Detailed Guide to BIM Drafting Services In today’s construction industry, Building Information Modeling (BIM) Drafting Services have become essential for efficient, accurate, and cost-effective project execution. This blog delves into the key aspects of BIM Drafting Services, answering why they are important, where they can be applied, and what they entail. Why Are BIM Drafting Services Important? Time Efficiency BIM Drafting Services streamline workflows, reducing the time required to complete projects. By providing accurate models and data, they help in faster decision-making and execution. Cost Savings With features like clash detection and resource optimization, BIM services minimize errors and reduce rework, leading to significant cost savings. Precision and Accuracy From working drawings to shop and GFC drawings, BIM ensures high precision, which is vital for seamless construction processes. Improved Collaboration BIM fosters better coordination among architects, engineers, and contractors by providing a single platform for all project data, reducing miscommunication and errors. Enhanced Quality By adhering to international standards and codes, BIM Drafting Services ensure superior quality in design and execution, improving overall project outcomes. Where Are BIM Drafting Services Used? BIM Drafting Services are versatile and can be applied across various sectors and project types. Some common areas include: Residential Projects From single-family homes to large apartment complexes, BIM is used for designing, planning, and optimizing residential construction. Commercial Buildings BIM is widely applied in offices, retail spaces, and mixed-use developments to ensure efficient design and resource management. Infrastructure Projects For bridges, roads, tunnels, and other infrastructure projects, BIM provides detailed modeling and facilitates better planning and execution. Healthcare Facilities Hospitals and clinics benefit from BIM’s precise design capabilities, ensuring compliance with healthcare standards and improving functionality. Educational Institutions Schools and universities utilize BIM for effective space planning, safety compliance, and long-term maintenance strategies. Industrial Projects Factories, warehouses, and other industrial facilities leverage BIM for efficient layout planning and resource optimization. What Do BIM Drafting Services Include? BIM Drafting Services cover a wide range of tasks and deliverables, tailored to meet specific project requirements. Here’s what they typically involve: 3D Modeling Detailed 3D models integrating architectural, structural, and MEPF elements provide a comprehensive view of the project. Quantity Takeoff (QTO) Accurate calculation of materials and resources, including door schedules, window schedules, wall schedules, and area calculations, helps in budgeting and procurement. Working Drawings High-quality working drawings, shop drawings, and GFC (Good for Construction) drawings ensure precise implementation on-site. Clash Detection Advanced clash detection tools identify and resolve conflicts between different design elements, reducing errors and rework. 4D BIM Integration By incorporating time-related data, 4D BIM offers insights into project scheduling and workflows, helping in effective time management. Why Choose Acura BIM Drafting Services? At Acura, we pride ourselves on delivering top-notch BIM Drafting Services tailored to your needs. Here’s why we stand out: Why Choose BIM Drafting Services?BIM Drafting Services not only enhance the quality and efficiency of construction projects but also provide an innovative approach to problem-solving. By incorporating cutting-edge technology, these services minimize human error, optimize resource allocation, and streamline communication across all project stakeholders. As a result, BIM reduces costly delays, improves project coordination, and ensures that the final output aligns closely with the initial vision. Whether you’re handling a complex commercial development or a residential renovation, BIM’s ability to integrate diverse data sets into one cohesive model allows for more accurate planning, better risk management, and smoother execution, all contributing to an overall reduction in project costs and timelines. Experienced Team: Our professionals are skilled, creative, and committed to tackling challenging projects. Cost-Effective Solutions: We offer high-quality services at competitive prices. International Standards: Adhering to industry codes and ethics, we ensure world-class quality. Comprehensive Support: From initial consultation to project completion, our team is with you every step of the way. Conclusion: Why BIM Drafting is Essential for Construction BIM Drafting Services are transforming the construction industry, offering unparalleled efficiency, accuracy, and cost savings. Whether you’re planning a residential project, a commercial building, or an infrastructure development, BIM can help you achieve your goals with precision and ease. Looking to outsource BIM services? Contact Acura today and let our experts assist you in simplifying your construction projects with innovative BIM solutions! Facebook Instagram Linkedin
5 Key Benefits of BIM Drafting Services for Construction Read More »