How can modern technology be leveraged to make architecture and planning more efficient and effective?
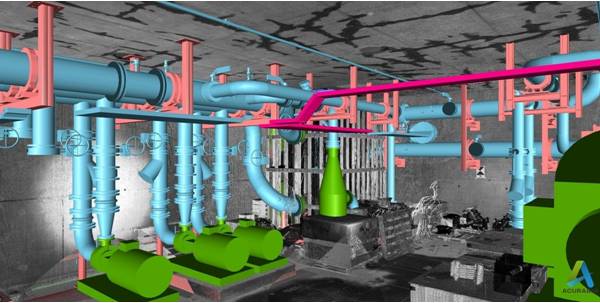
Modern technology offers numerous opportunities to make architecture and planning more efficient and effective. Here are several ways technology can be leveraged in these fields: Building Information Modeling (BIM): BIM is a digital representation of a building or infrastructure project that encompasses geometry, spatial relationships, geographic information, and other relevant data. BIM enables architects, engineers, and construction professionals to collaborate and share information seamlessly. It enhances efficiency by allowing real-time updates, clash detection, and simulation of various design scenarios. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR technologies provide immersive experiences that can revolutionize architectural design and planning. Designers and clients can visualize projects before they are built, walk through virtual spaces, and make real-time modifications. VR and AR also aid in detecting design flaws, optimizing layouts, and communicating design intent effectively. Geographic Information System (GIS): GIS technology integrates spatial data, such as topography, land use, and infrastructure, with planning processes. It helps architects and urban planners analyze and visualize data, assess site suitability, identify environmental constraints, and optimize land use patterns. GIS facilitates informed decision-making and promotes sustainable development. Parametric Design and Computational Tools: Parametric design software allows architects to define relationships between design parameters and automate design processes. By using computational tools, architects can generate complex and innovative designs quickly. These tools enable optimization, performance analysis, and exploration of design variations, leading to more efficient and sustainable architectural solutions. 3D Printing and Prefabrication: Additive manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing, enable architects to create intricate models, prototypes, and even full-scale building components. This technology accelerates the design iteration process, reduces material waste, and allows for customization. Prefabrication techniques leverage technology to produce building components off-site, enhancing efficiency, quality control, and construction speed. Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Cities: IoT devices embedded within buildings and urban environments collect and exchange data to improve efficiency, safety, and sustainability. Smart city initiatives employ IoT sensors for energy management, traffic optimization, waste management, and infrastructure monitoring. This data-driven approach enhances planning processes, enabling evidence-based decision-making and resource optimization. By leveraging these technologies, architects and planners can streamline their workflows, enhance collaboration, improve decision-making, and create more efficient, sustainable, and effective built environments.