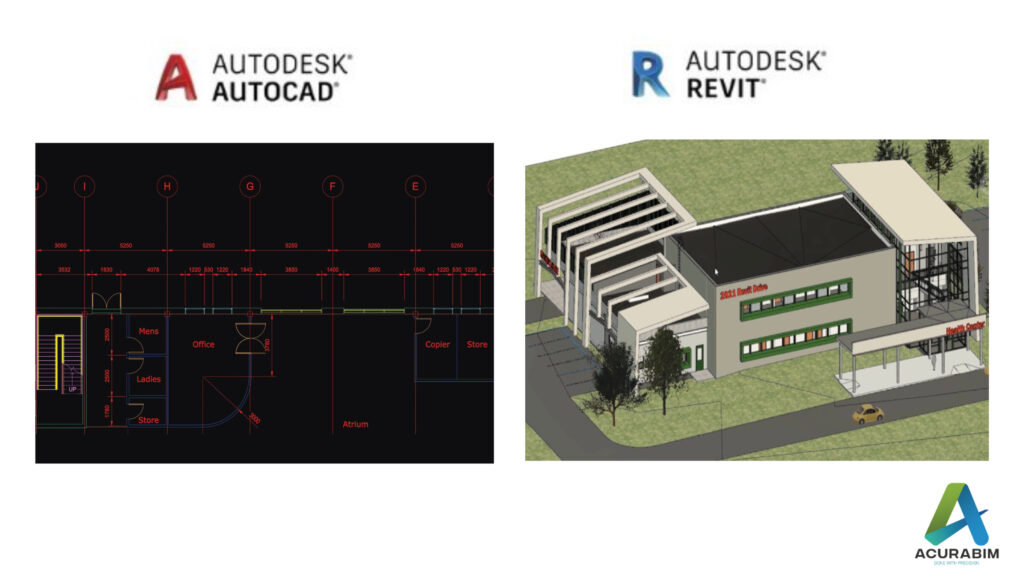
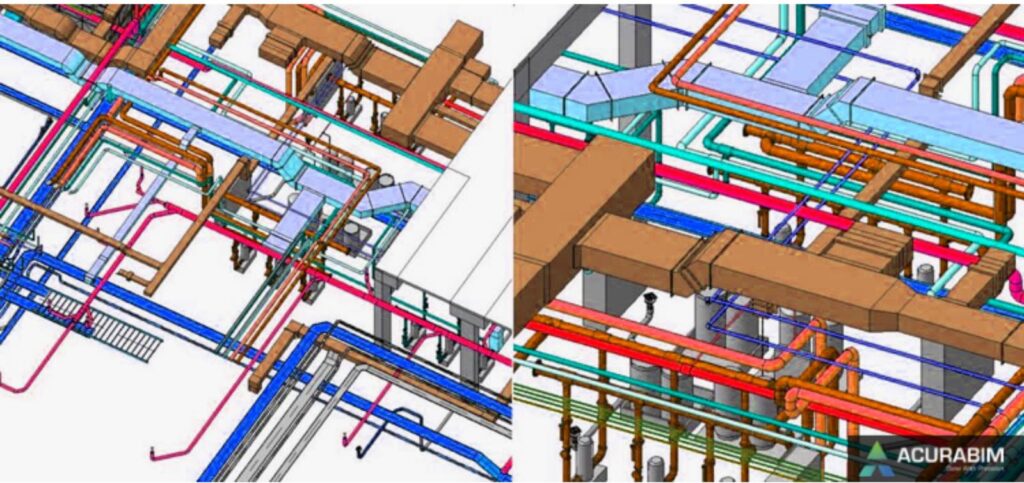
To make sure that design problems are fixed and in compliance with building standards and norms, a method called “Revit clash detection Process” checks collisions (also known as “clashes”) and interference. Both Navisworks and Revit are used for this procedure. BIM Engineers can find the clashes and certify the design without harming compliance by performing clash detection in Revit. To make sure that all the parties approve the changes and the clashes are resolved without further conflict, the resolution of the clashes is highlighted and discussed in a BIM coordination meeting with all the Design Engineers of different disciplines, the architect, engineer, contractors, and the builder. Because it can produce schedules, location-specific clashes, and other useful information, Revit Drafting Services is a great choice for validating designs through clash detection. Revit provides helpful collision detection tools, which show conflicts based on the interference of the objects and emphasise them when necessary. However, it is not particularly capable of producing reports, offering a state of clashes, creating rules, or offering tests for clearance and custom clashes, among other things. Other software can be used to carry out these operations. However, a business or team that is tackling clash detection for the first time and is still completing interference tests can move forward with Revit. Revit clash detection is sufficient even for little projects. Revit and Navisworks can both handle complex clash detection. Even though building firms and MEP contractors prefer Navisworks, clash detection in Revit offers several benefits. The following are top advantages of Procedure of Clash Detection in Revit’s and Navisworks. Reducing Wasteful Building Time By detecting collisions in the pre-construction stage, the Revit Clash Detection service reduces unnecessary construction time significantly. We may export the model to Navisworks to extract conflict reports after clash detection in Revit. Conflicts can be handled in some cases by making small adjustments and in others by holding group sessions. Whenever necessary, we may check the design and make changes. The earlier these processes are finished; the more construction time is saved after the production designs are sent to the on-site engineer. The design has not changed, and the installation is nearly complete on schedule. Reduces Construction Costs Prior to the development of BIM, managing construction costs and construction time posed serious problems. There have been instances where conflicts arose during on-site construction and had to be addressed before building could continue. Over time, design modifications were made, and it was difficult to gather all the agencies for the conference. Because of the prolonged building period and underutilization of the work force, construction firms and builders suffered significant losses. However, with the aid of BIM clash detection services, the model can be created in Revit, and any conflicts may be handled through online meetings and model sharing in a cooperative manner. Process toward Design Validation: Revit Clash detection makes it simple to handle design errors. The designs may be compared and coordinated when the 3D model is complete to see if the architectural, structural, and MEP services disciplines are in accordance with the standards and are coordinated with one another. Type of Clash Detection : Two types as stated below The number of interferences existing in a 3D model of the current design have been counted, examined, and recorded thanks to clash detection in Revit. This method is useful for assessing recently begun or completed (as constructed) projects. It significantly lowers the error-index, which lowers the project’s total productivity and length of construction. As we have a report of the BIM components or model pieces clashing with each other, we can run simple interference tests. Using connected architectural and structural models or linked MEP and structural models, these conflicts may be verified as a single file. When we do conflict detection, three different types of confrontations may be seen. There are three different types of confrontations that might occur: Hard clashes, soft clashes, and Workflow problems. Some conflicts must be disregarded and investigated on the spot. However, certain disputes must be settled before building may continue. Hard Clash Detection Method A hard clash happens when elements from two disciplines cross across. For instance, Hard collisions occur when beams and columns strike ducts, or when the ducts strike the ceiling or doors. Lack of coordination between MEP engineers or architects and structural engineers is the primary cause of serious collisions. Such conflicts may also be caused by improper modelling. Collaborative discussions, design modifications, and, in the end, modifying the BIM Models to reflect the design modifications are used to settle such conflicts. The clash detection procedure is used after remodelling. The embedded data principle is adhered to by BIM modelling software like Revit, which aims to minimise such conflicts at the modelling stage itself. Soft Clash Detection Method These conflicts happen when two disciplines don’t have enough room to move apart, causing one BIM object to overlap the other. Increasing or lowering the area available to accept the items can be used to avoid such collisions. Inference: We have seen a number of advantages of employing clash detection in Revit as well as its need. Even though Navisworks is a programme that is better suited for interference checks and reporting, Revit aids in conflict detection. Depending on the severity, the clash data may then be transferred to Navisworks for additional processing. The optimum method for conflict detection would be to start with Revit, assess the clashes, and then export the model to Navisworks. Get the reports by doing a thorough Navisworks clash detection. Have a meeting to discuss the design adjustments while reviewing the findings. Make the necessary adjustments in various disciplines based on the outcomes of the meeting to make sure the models are prepared for the extraction of the coordinated production drawings.