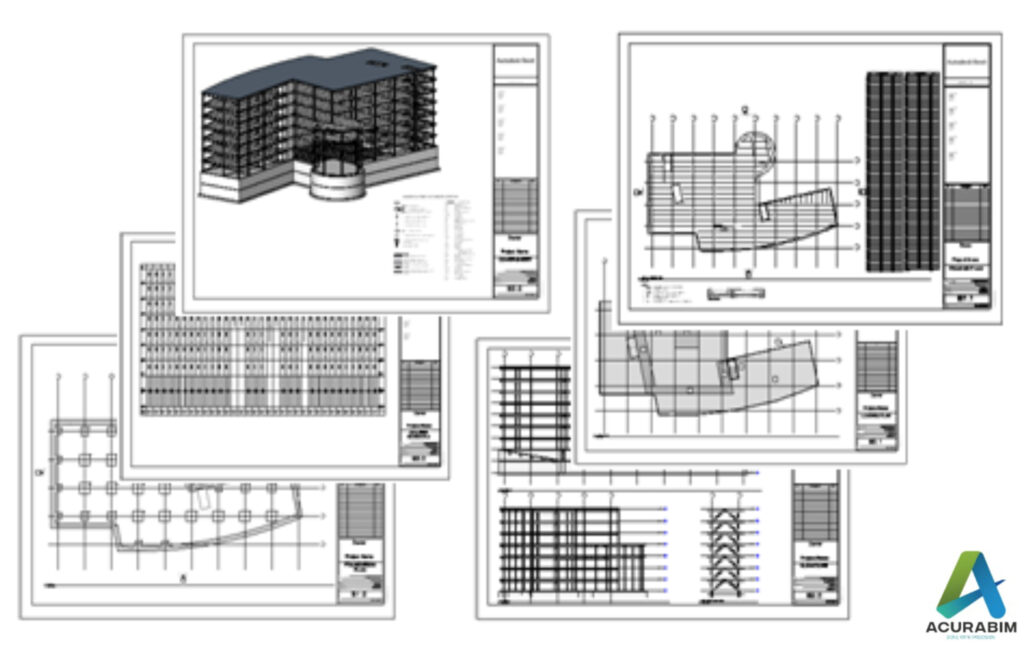
Export Sketchup file to Google Earth
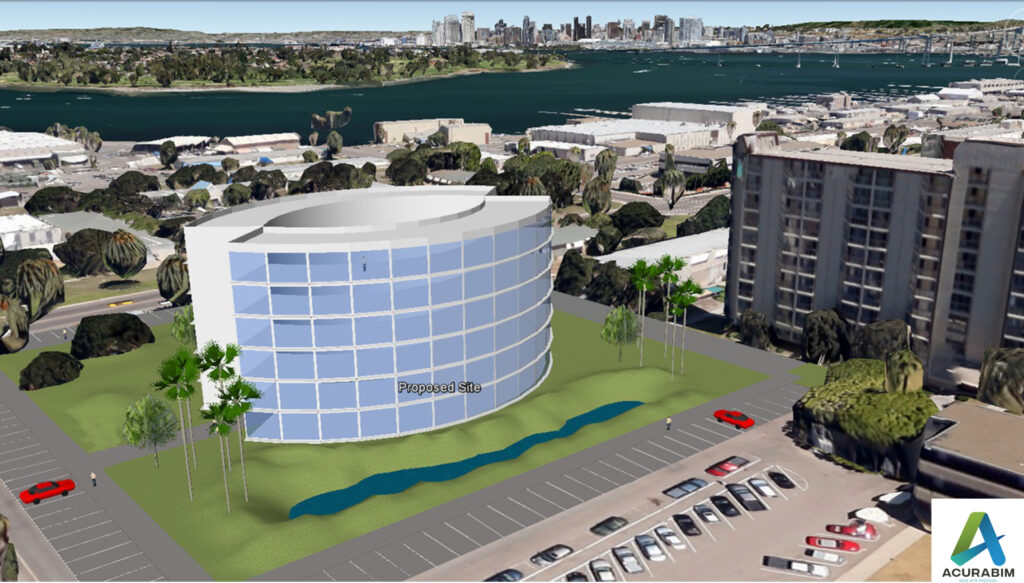
Introduction: SketchUp is a powerful 3D modelling software that is widely used by architects, designers, and other professionals in the construction and design industry. One of the great features of SketchUp is the ability to export your model to Google Earth, allowing you to view your design in a real-world context. Exporting a SketchUp file to Google Earth is a simple process that can be done in just a few steps. Make sure that you have both SketchUp and Google Earth installed on your computer. Sketchup file is converted to KML file, & thus that file Is imported in Google Earth. A brief explanation for KML file is given in following para. About KML File: A KML file is a type of file that is used to store geographic data and information in a format that can be easily read by a variety of mapping and spatial analysis software. KML stands for “Keyhole Markup Language,” and it is a file format that was developed by Google for use with its Google Earth software. One of the key features of KML files is that they allow you to store and display geographic data in a way that is easily understood by both humans and computers. KML files use a system of tags and attributes to describe the data that they contain, and this makes it easy for software programs to interpret and display the data in a meaningful way. There are many different types of data that can be stored in a KML file, including points, lines, and polygons that represent features on the earth’s surface, as well as information about the appearance and behaviour of these features. For example, you can use a KML file to store information about the location and appearance of a building, or you can use it to store data about a network of roads or a set of geographic boundaries. KML files are often used in a variety of applications, including GIS software, mapping websites, and mobile apps. They are also commonly used to share geographic data with others, as KML files can be easily shared and viewed by anyone who has access to a KML-compatible application. Overall, KML files are an important tool for storing and sharing geographic data, and they are widely used in a variety of fields, including geography, mapping, and spatial analysis. Whether you are working on a professional project or simply exploring the world around you, KML files can be a valuable resource for understanding and visualizing the earth’s surface. To export your SketchUp file to Google Earth, follow these steps: Open your SketchUp model in SketchUp. Go to the “File” menu and select “Export.” In the export dialog box, select “Google Earth (KML)” as the file type. Choose a location to save the KML file, and click “Export.” Open Google Earth and go to the “File” menu. Select “Open,” and choose the KML file that you just exported from SketchUp. Your SketchUp model will now be displayed in Google Earth, allowing you to view it in the context of the real world. You can use the navigation tools in Google Earth to pan, zoom, and rotate your model, and you can also use the layers panel to turn different elements of your model on and off. Summary: Exporting a SketchUp model to Google Earth is a great way to share your design with clients and colleagues, and it can also be a helpful tool for visualizing your design in a real-world context. Whether you are working on a residential project, a commercial building, or any other type of design, exporting your SketchUp model to Google Earth can be a valuable part of your workflow.
Export Sketchup file to Google Earth Read More »